


At Petroperú, we maintain a Contingency Plan designed to respond effectively to environmental emergencies, minimizing their impacts and restoring the surroundings to their original conditions. This plan is in strict compliance with the Regulation for Environmental Protection in Hydrocarbon Activities (Supreme Decree No. 039-2014-EM) and other applicable regulations.
Our Contingency Plan establishes protocols for spill containment and confinement, followed by actions for recovery, cleanup, environmental remediation, and final waste disposal. Throughout the process, constant monitoring is conducted of water bodies, soil, sediments, as well as affected flora and fauna.
In the event of an emergency, we activate this plan with the participation of companies specialized in environmental response, ensuring immediate and effective intervention. We also perform follow-up monitoring to verify the achievement of our environmental objectives and guarantee the recovery of impacted areas.
In case of spills, the recovery and degradation of the hydrocarbon are achieved through the deployment of various techniques which, collectively, allow the remediation of affected environmental components. The effectiveness of interventions is periodically monitored throughout the remediation process and after its completion.
General framework of activities – ONP Contingency Plan
Additionally, in the occurrence of any type of environmental emergency, the Company will issue the corresponding report to OEFA and other competent authorities according to the currently valid risk estimation methodology[1], which is based on the evaluation of specific criteria related to environmental protection.
In 2024, 41 environmental emergencies were reported, of which the majority occurred in Block Z-69 (15 cases), followed by Block 192 (Loreto) and ONP (7 cases each), among others.
In contrast, in 2023, 88 reportable environmental emergencies were recorded according to OEFA criteria, of which 61 % occurred in Block 192, evidencing a reduction in the total number of incidents in 2024. Also, 5 emergencies related to natural gas distribution systems were recorded in the southern part of the country.

The main causes of environmental emergencies were third-party actions in 36.6 % of cases (18 cases), material failures (5 cases), and maintenance-related incidents (3 cases), while in three events the cause is still under investigation.
Environmental emergencies by type 2024
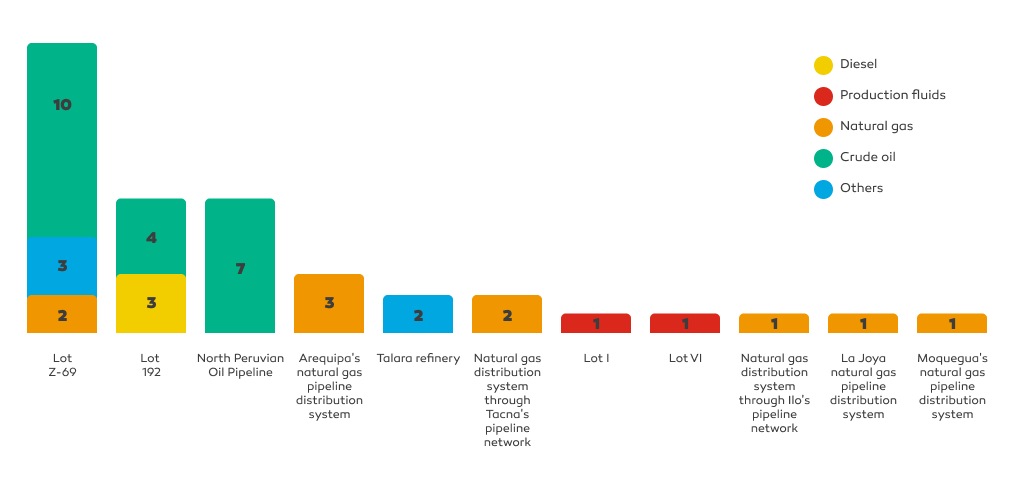
Environmental emergencies 2024 reported by number of barrels 1/
| Location | < 1 BLS | 1 to 10 BLS | 10 to 100 BLS | > 100 BLS | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LOT 192 | 1 | 5 | 1 | 7 | |
| LOT I | 1 | 1 | |||
| LOT VI | 1 | 1 | |||
| ONP | 4 | 2 | 1 | 7 | |
| RTAL | 2 | 2 | |||
| Z-69 | 11 | 1 | 12 | ||
| Total | 14 | 12 | 3 | 1 | 30 |
Environmental emergencies 2024 reported by number of barrels 2/
| Location | < 1 BLS | 1 to 10 BLS | 10 to 100 BLS | > 100 BLS | Total |
| LOT 192 | 1 | 5 | 1 | 7 | |
| LOT I | 1 | 1 | |||
| LOT VI | 1 | 1 | |||
| ONP | 4 | 2 | 1 | 7 | |
| RTAL | 2 | 2 | |||
| Z-69 | 11 | 1 | 3 | 15 | |
| Syst. Dist. Natural Gas (*) | 8 | 8 | |||
| Total | 14 | 12 | 6 | 9 | 41 |
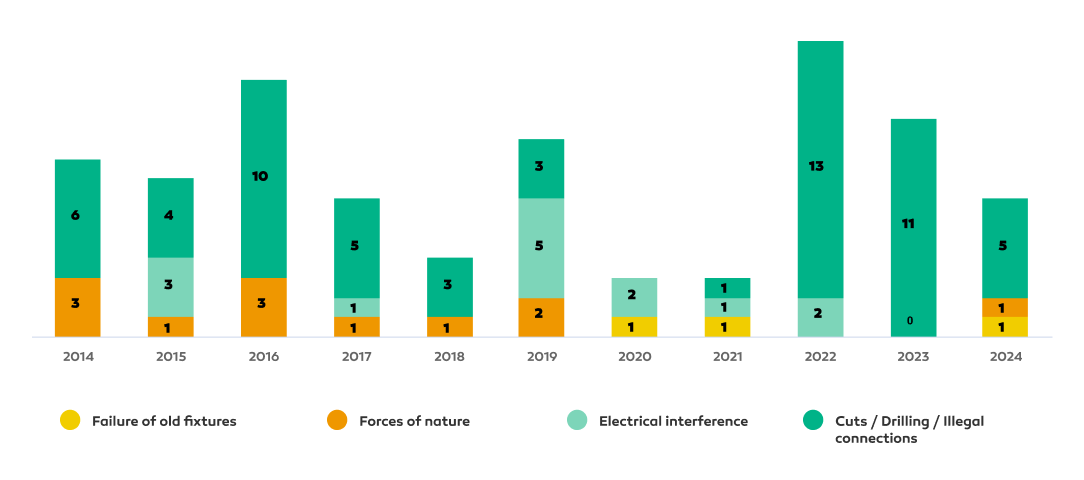
In the specific case of the North Peruvian Pipeline, between 2014 and 2024, 90 incidents occurred on the ONP pipeline, of which 83.3% were due to third-party incidents, 13.3% were due to natural forces, 2.2% were due to accessory failures, and 1.2% were due to material failures. During 2024, 7 environmental contingencies were recorded, of which 71.4% were caused by third parties, 14.3% by geodynamic phenomena, and 14.3% by material failures. This represents a lower number of contingencies compared to 2023, a period that recorded 11 environmental emergencies, 100% of which were perpetrated by third parties.
North Peruvian Oil Pipeline Contingencies 2014-2024
The Company makes available the statistics of ONP contingencies on the following website: https://oleoducto.petroperu.com.pe/plan-contingencia/estadisticas/